A Complete Guide to How to Recover from Google Penalty

Google penalties are a nightmare for any website owner. When Google finds that a website has violated its rules and algorithms, they punish it in various ways. This could low down the website’s ranking or remove it from the search engine.
So if you ever experience a massive sudden drop in traffic to your website, it may be a result of Google penalties. But recovering Google penalties isn’t an easy task. You must know the right strategies and approaches to do that.
Understanding why your website got penalized is the first step toward recovery. In this article, we’ll cover a detailed analysis explaining all the possible ways for Google penalty recovery. Let’s get started.
Table of Content
What is Google Penalty and Its Major Types?
How to Check Google Penalty on Your Website
Proven Tips and Techniques on How to Recover from Google Penalties
FAQ on How to Recover from Google Penalty
Final Takeaways!
What is Google Penalty and Its Major Types?
Google penalty is a punishment against a website that engages in manipulative activities and violates the guidelines of Google Search Console. Google penalizes the guilty websites in many ways. And its ultimate result is a massive loss of traffic.
Plus, it can negatively affect your overall online presence. There are various types of Google penalties and we can classify them into two categories: algorithmic and manual. We’ve covered in detail how to solve them in later parts of the article. Let’s now take a quick look at the types of Google penalties.
01. Algorithmic Penalties

Algorithmic penalties are the punishments automatically triggered and imposed on a website when it violates the specific search engine algorithmic rules and guidelines. Some major Google algorithmic penalties are:
a. Panda Penalty – Targets those websites filled with mediocre, thin, and duplicate content. It also penalizes the websites publishing excessive ads.
b. Penguin Penalty – Penalizes the websites involved with manipulative link-building practices, like paid links and irrelevant backlinks.
c. Mobile-Friendly Penalty – Websites that aren’t properly optimized for mobile devices and use spammy mobile redirection are at risk of getting this penalty.
d. Core Web Vitals Penalty – Websites failing to meet the minimum user experience, page loading speed, and visual aesthetics face the penalty.
02. Manual Penalties

Manual penalties are imposed by human staff after manually reviewing a website. The same rules and guidelines that are followed in algorithmic penalties are also followed here. Some major manual penalties are:
a. Unnatural Link Penalty – This penalty is imposed on websites that are involved in a spammy and manipulative link-building process.
b. User-Generated Spam Penalty – Trying to promote web content through fake comments, fake reviews, and fake profiles in different forums and websites is counted as user-generated spam.
c. Cloaking Penalty – This penalty is triggered when a website tries to rank its posts and pages on search engines through deceptive content.
d. Hacked penalty – If a website contains harmful content due to hacking, Google imposes a penalty to protect visitors from potential damages.
How to Check Google Penalty on Your Website
Without identifying the specific cause of why your website has been penalized, you can take recovery actions correctly. Here’re some best possible ways you can follow to check if there is a Google penalty on your website.
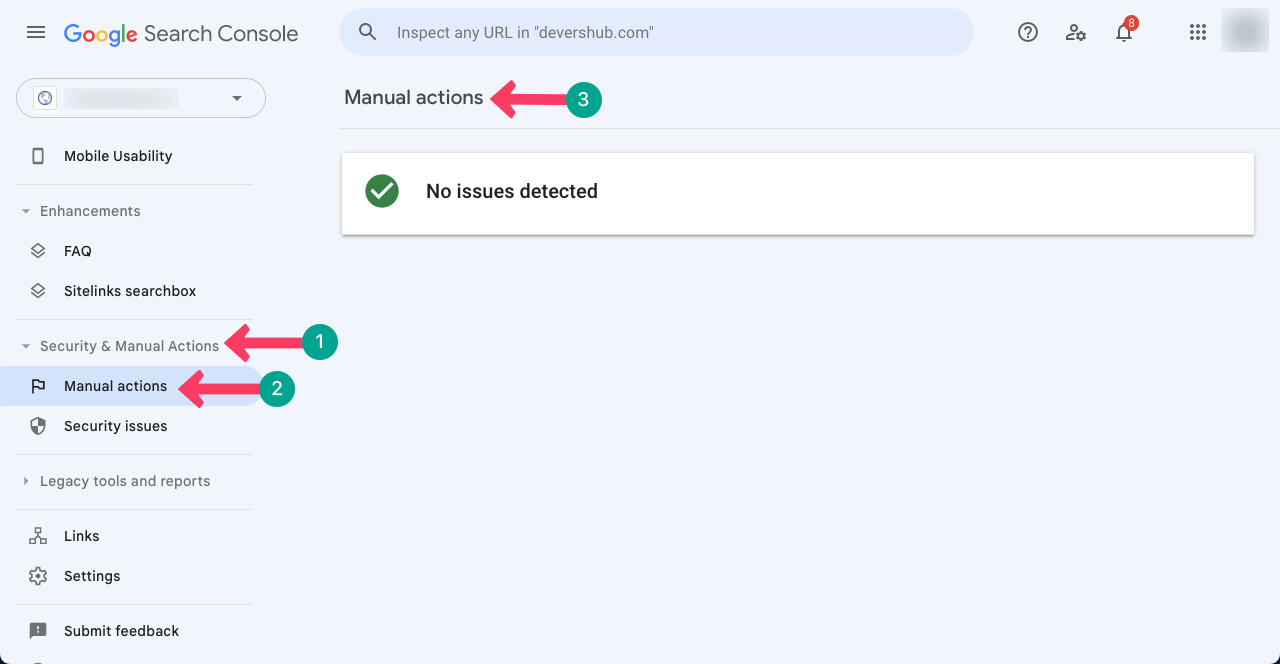
Step 01: Visit Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool provided by Google to know if the search engine has imposed any manual penalty on your site.
- Go to Google Search Console.
- Open with your domain.
- Navigate to Security & Manual Actions > Manual actions.
- You’ll see the site under the Manual actions section if the site is penalized.
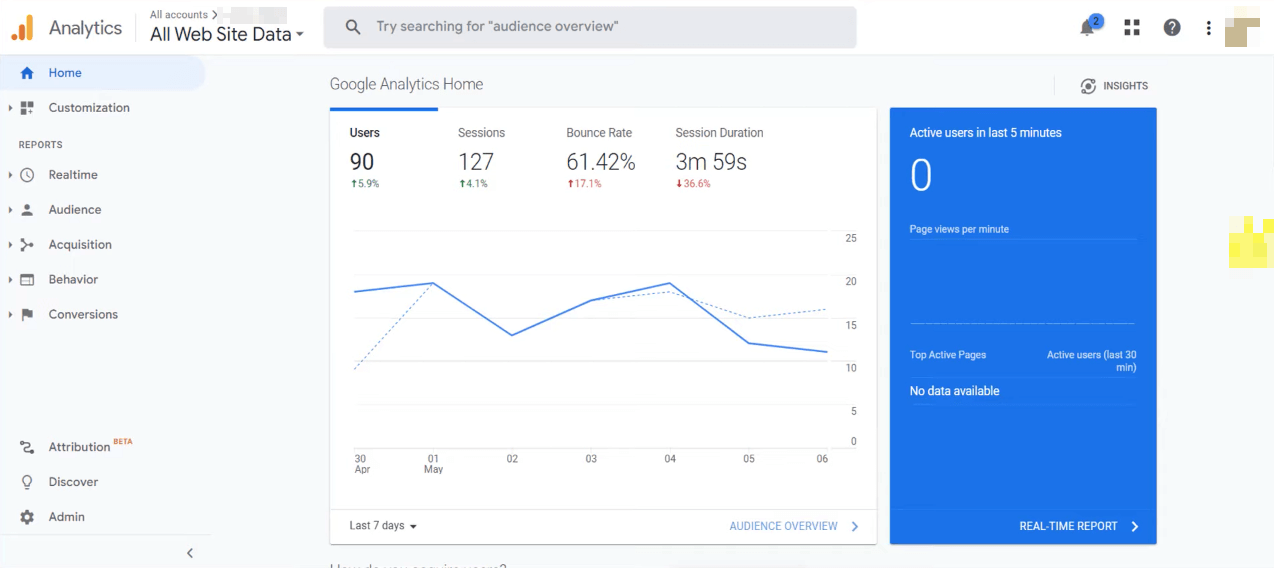
Step 02: Analyze Traffic Using Google Analytics
We already said once that a sudden drop in traffic flow indicates Google’s penalty. Google Analytics is another free tool by which you can check the organic traffic flow to your website.
- Open Google Analytics with your website.
- Check the traffic history.
- Mark the date from which the traffic is flowing.
Step 03: Check Recent Algorithm Updates
Google comes with algorithmic updates every few days, weeks, or months and rolls them out over all the indexed websites online. Websites that fail to align with the core update rules and requirements get penalties.
- Check the Google Core update releasing dates.
- Cross-check if your web traffic started dropping the releasing date of any particular update.
- If two intersect, you can count your website has got an algorithmic penalty.
Step 04: Run an SEO Audit
Running an SEO audit can help you identify potential issues that might have triggered a penalty. Some common issues can be thin content, duplicate content, keyword stuffing, technical issues, poor website performance, etc.
Below are some best Google penalty checker tools you can use to run SEO audits.
- SEMrush
- Mozcast
- Moz Pro
- Ahrefs
- Rank Ranger
Proven Tips and Techniques on How to Recover from Google Penalties
Recovery from Google penalties may take you time. It depends on how serious the problem is and how many issues you have to fix. We’ll now cover all the common problems that trigger Google penalties with proven tips and techniques to recover from them.
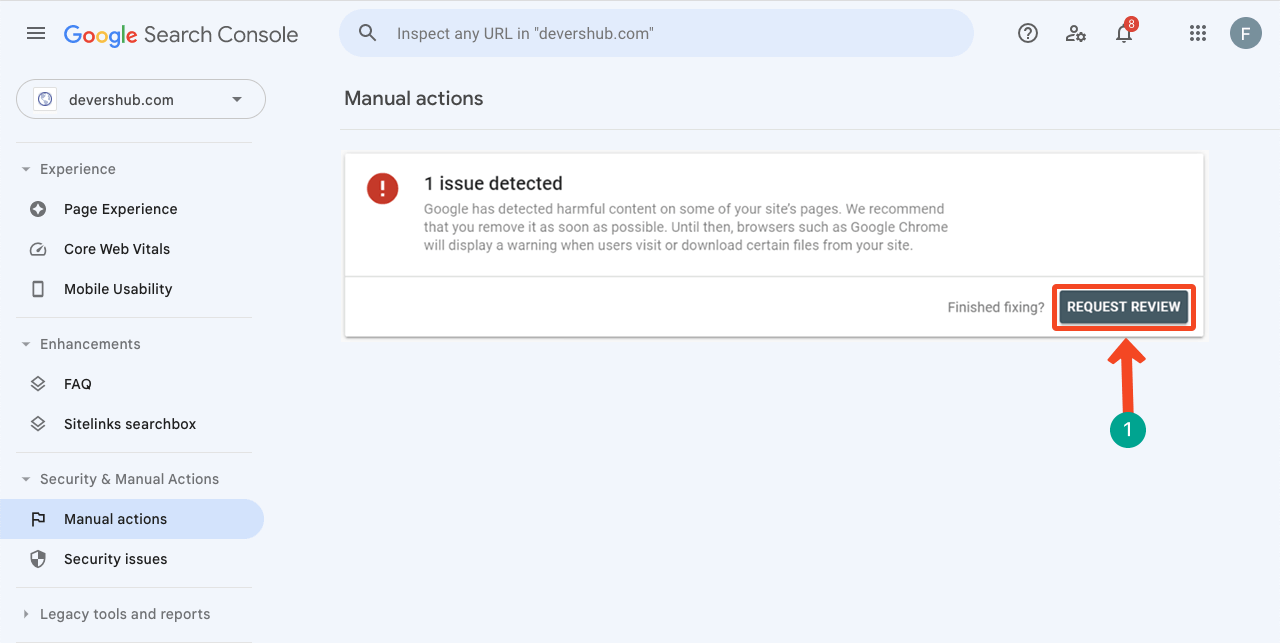
Tip 01: Request Review in Google Search Console
If Google gives you any manual penalty, you’ll see it with a notification ‘issue detected’ in Google Search Console. Clicking on the notification will give you a detailed report. Fix the problem and press the Request Review button at the end.
If you successfully fix the notified problem(s), Google will withdraw the penalty within a few hours or days.
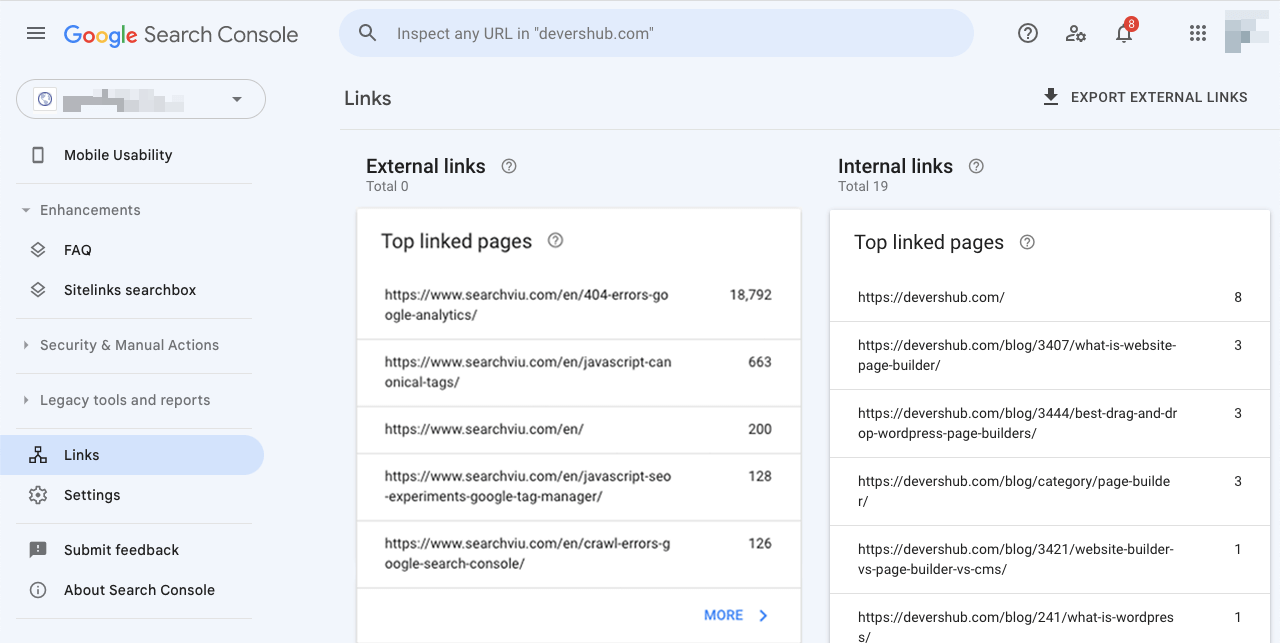
Tip 02: Clean Up Unnatural Backlinks
Unnatural backlinks are also known as manipulative or spammy external links managed through unethical means. They are often purchased or built by spammers. You can find the list of all external links from the Google search console.
- Open your Search Console.
- Go to the Links section.
You’ll get the links of external links. But this free tool won’t tell you which ones are unnatural. You have to check them manually.
But SEMrush is an exciting tool by which you can audit all your external links and find out the unnatural ones. They usually term these links as ‘Toxic Links‘.
- Open SEMrush.
- Go to the section Backlink Audit.
- Add your Domain and search.
- It may take several minutes to complete the audit.
- You’ll get a below-link report at the end.
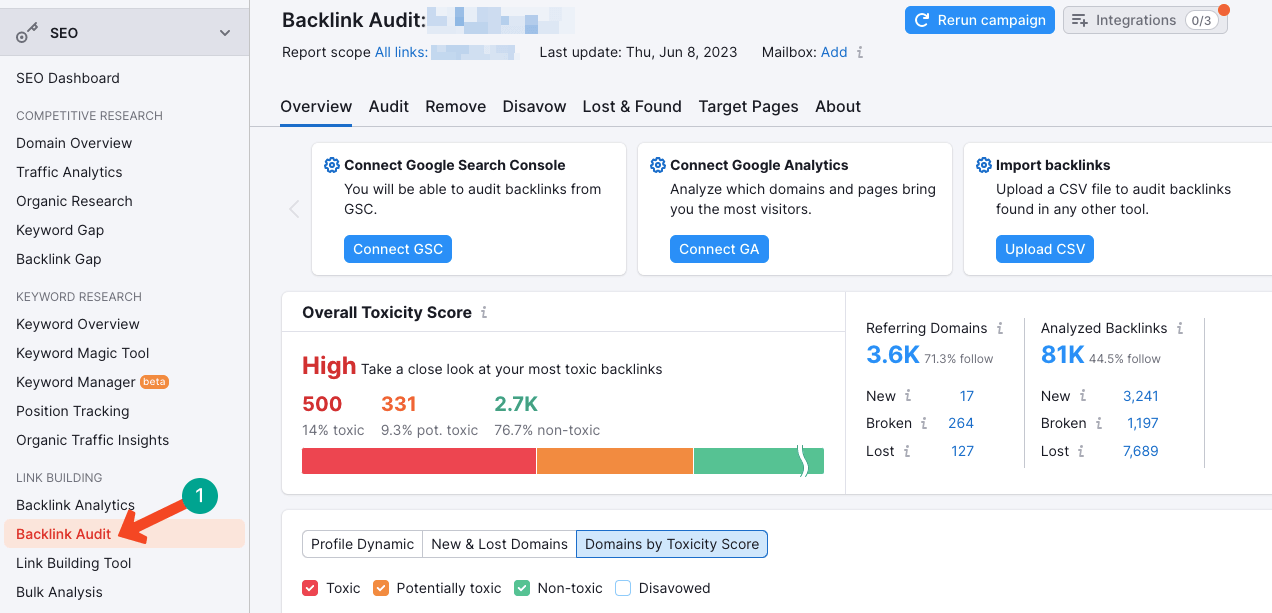
Create a list of the toxic and potentially toxic backlinks. Next, go to the Disavow Link page of Google Search Console. The page will provide a step-by-step guide on uploading the backlink list and starting the disavowing process. This will free your website from unnatural and toxic backlinks.
Tip 03: Remove Cloaking and Sneaky Redirects
Cloaking and sneaky redirections are black-hat SEO practices. They are used to promote content on search engines in deceptive ways. Suppose one has searched with the keyword ‘best Samsung smartphones’ and your web page has appeared on the top page.
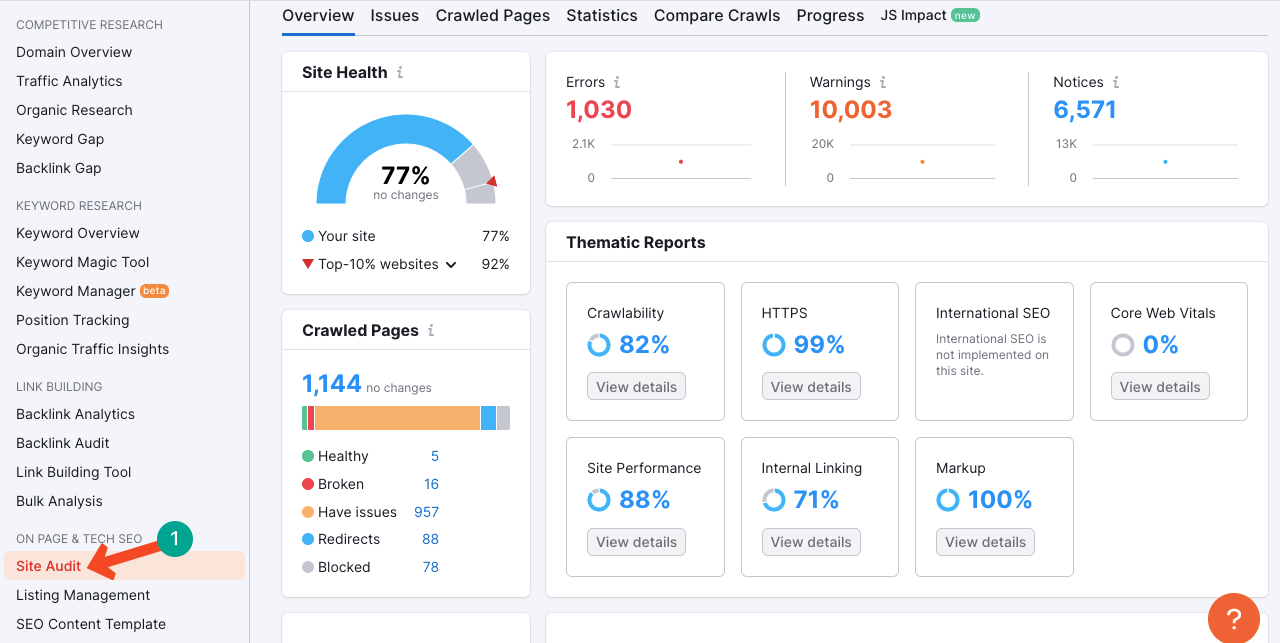
But users are shown completely different products or information unrelated to mobile phones when they click it. There is no specific tool to track successfully track all the cloaking and sneaky redirects as they are carried out deliberately. However, SEMrush can help you a bit.
- Open SEMrush.
- Navigate to Site Audit.
- Set up a new project.
- Type your domain address.
- Start the audit.
This may take several minutes. Once the audit ends, explore the Redirects and Have Issues sections. Find out the issues causing sneaky and cloaking redirects. Sit with SEO experts or developers to solve them.
Explore the best link-building strategies to grow organic traffic flow.
Tip 04: Solve AMP Content Mismatch
AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages. Google introduced this framework to optimize and fast-load web pages on mobile devices. But when an inconsistency arises between the content displayed on the regular web page and the corresponding AMP version, it’s identified as a content mismatch.
Google usually notifies about the AMP penalty in the search console. Incorrect implementation of AMP, errors in the markup, using incompatible themes and templates, and custom modifications may cause this problem.
If you are a non-technical person with limited knowledge, you better take developers’ help to solve the problem.
Tip 05: Erase Hidden Text and Keyword Stuffing
Hidden texts refer to content only search engines can crawl but readers and visitors can’t see. This is usually carried out by matching the text color to the background color, adding words behind the images, and reducing the font size.
The sole objective of this practice is to add as many keywords as possible to rank up in search engines. Keyword stuffing involves inserting keywords and relevant phrases repeatedly in unnatural ways. Google strongly prohibits these practices.
While you may benefit temporarily in this process, Google may permanently downgrade your site once they catch it. So rely on the natural content creation process with semantic SEO.
Tip 06: Take Your Site Out from Spammy Hosts

Spammy Hosts are the servers that host a significant number of low-quality websites that deliberately carry out spammy activities. These hosting servers either have inadequate security measures or are also involved in spamming.
Google will penalize you if your website is hosted on such a server. So try to host your website on a well-recognized server. If you’re already hosting somewhere that isn’t much popular, check whether there is any hosting-related notification in the search console.
If thorough investigations conclude your hosting server is involved with spamming, move somewhere else immediately.
Tip 07: Resolve Structured Data Issues
Structured data is a set of standardized formats that help Google quickly understand and index particular types of content. FAQ, review, local address, how-to schema, product, event, recipe, breadcrumbs, videos, etc., are the most popular structured data.
Search engines also love structured data, enabling them to enhance search results with rich snippets and other features. But if they are implemented incorrectly and violate Google’s guidelines, it can result in penalties.
Below are some key structured data guidelines introduced by Google:
- Relevant the data with your post and page content.
- Never show deceptive information with keyword stuffing.
- Recheck the data after every website update so they work fine.
- Make sure each individual content uses a separate markup.
Note: Example of the last point. If you are listing multiple products, you must use a separate markup for each product. Incorporating multiple products in the same structured data markup will confuse the search engine.
Tip 08: Improve Thin Content or Delete Them If Unnecessary
Thin content refers to web posts and pages with little or no user value. They usually lack originality, relevance, depth, and ability to provide solutions. Duplicate content also belongs to the thin content category.
Google promotes highly informative content and provides comparatively better solutions than others. So if you still focus on generating thin content, it will be a waste of time. Plus, Google has a special policy to penalize duplicate content.
But SEMrush can help you find duplicate content.
- Open SEMrush.
- Go to the Audit section.
- Type your domain and start auditing.
- Go to the Issues section afterward.
- You’ll get a report like the one below.
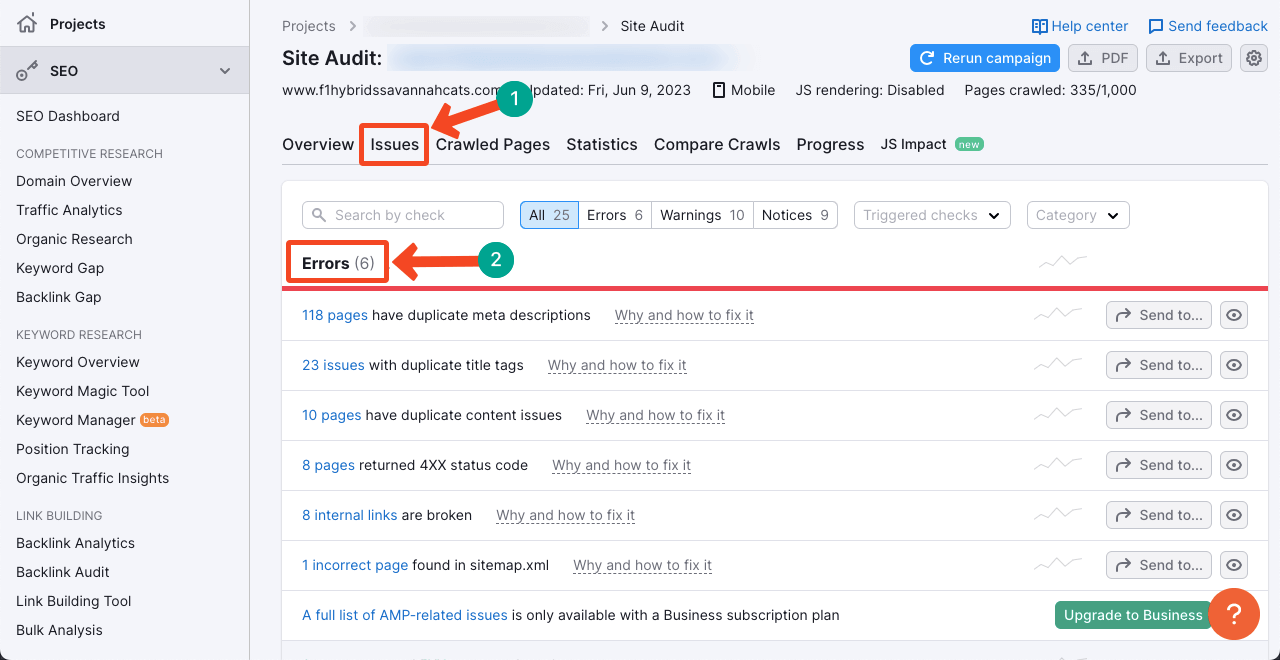
Tip 09: Stop the Incoming Flow of User-Generated Spam
User-generated spams are low-quality promotional content created by fake user profiles. This method involves promoting web content by submitting reviews and comments with links in the blog section of other websites, forums, and social posts.
Human users or spam bots may come to your website to deliberately do the spamming. Allowing them to make a way to your site indicates to Google you have vulnerability issues. Implement the following solutions to barricade this spam.
- Use an anti-spam security plugin.
- Use Captchas to filter out bot users.
- Review every user-generated content before publishing them.
- Regularly audit and cleanse spam content from your site.
FAQ on How to Recover from Google Penalty

We have tried our best to present all effective methods to recover from Google penalties in this article. Still, you may have some questions in your mind. We’ll try to cover them in the FAQ section.
How much time does it take to recover from the Google penalty?
The duration to recover from Google penalties varies depending on the severity of the violation. If the penalty is algorithmic, you may have to wait till the next update release even if you fix the problem.
Again, if the penalty comes manually and you submit a request, recovery time may take hours to weeks and months until the reviewer sees it.
Does Google penalize for illegal content?
There is no straight answer to this question. Actually, what is illegal in one country may not be illegal in other countries. So Google only restricts access to the particular content that isn’t legally allowed in particular regions.
Should I delete the content that got a Google penalty or improve it?
If the content is low-quality and violates any major guideline of Google, better to delete it. But if the content is of high quality and you have enough resources to recover from the penalty, then improving it is a good option.
What are the common mistakes people make when recovering from Google penalties?
1. Failing to identify the root cause
2. Not having enough knowledge about Google penalties
3. Rushing to the recovery process
4. Overlooking the technical aspects
5. Failing to communicate with Google
Will a website regain its previous rankings after recovering from Google penalties?
According to Google, site owners can expect to bounce back to the previous ranking state after recovering from the manual penalty. But if competitive websites come up with better content in the meantime, recovered websites may fall into a battle to retain their previous positions.
Plus, if penalties are algorithmic, the recovery phase may take a long time which can dilute the ranking potential, at least slightly.
Final Takeaways!
Penalties aren’t a new thing in the web industry. You’ll hardly find any established website never got a pental from Google in their entire lifetime. Google never gives penalties with the intention of destroying your website.
Rather they want to ensure the online space is a safe haven for all types of activities like eCommerce, education, career build-up, and more. So they regularly introduce new guidelines to protect online users from any potential harm.
A penalty imposed means some glitches on your site must be corrected. We’ve tried to cover all the latest tips and techniques by which you can recover from the penalties. If you benefited from this article, please let us know by commenting.
Disclosure: WP Hive earns a commission when you buy through partner links. It does not influence the unbiased opinions of our writers. Learn more →
https://wphive.com/tutorials/how-to-recover-from-google-penalty/
Fuad Al Azad
Fuad Al Azad is a creative writer who loves to blog on everything in between tech, marketing, and eCommerce. Alongside, he is an admirer of fact, fiction, and philosophy.



