WordPress User Roles, Explained under 5 min!
WordPress User Permissions help you to control how individual users interact with your website. It also sets a permission mechanism throughout your WordPress installation. You can also assign or modify roles for your website.
WordPress User Permissions enable you to easily manage and ensure the permission hierchy you want.
Why Should You Consider Using WordPress User Permissions?
When you are the only person running your site, you don’t need to think about WordPress User Permissions. But whenever you need to give other people access to your website, WordPress User Permissions are essential for controlling their activities.
You can ensure that no one has more power than they need through correctly applying for the user roles. WordPress User Permissions are important because-
- These help secure your WordPress site by ensuring that users don’t have access to things they shouldn’t have.
- These can help you to define your workflows. WordPress has pre-made user roles that you can apply to your team members or users to give them access to only the functionality they need to write or add WordPress posts.
Default WordPress User Permissions
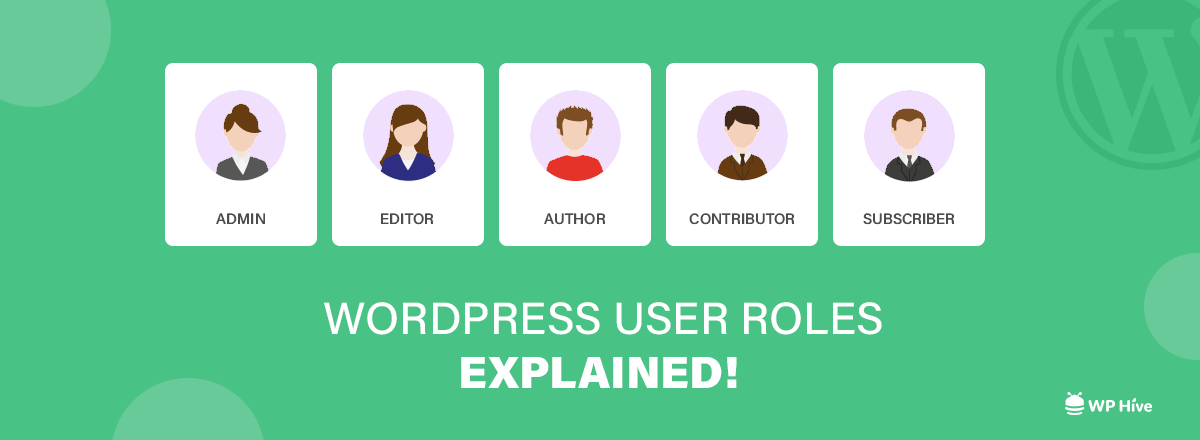
When you install WordPress, you will get six default user roles for you.
- Administrator
- Editor
- Author
- Contributor
- Subscriber
- Super Admin
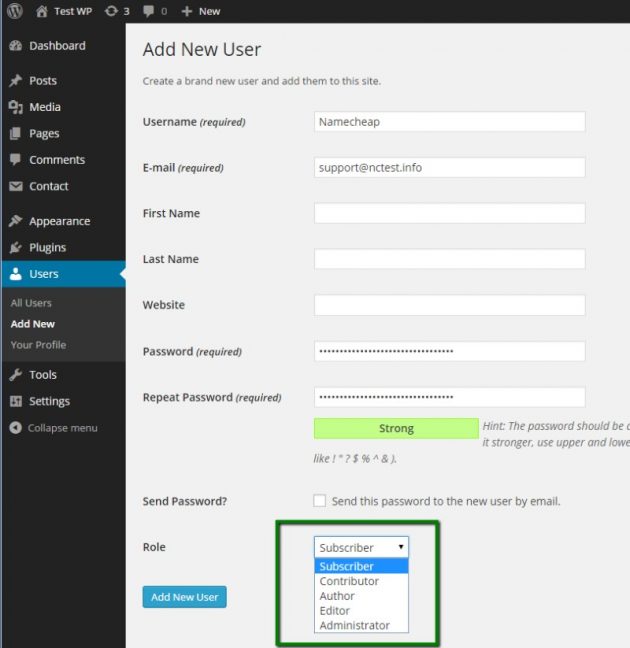
We are going to cover each of the user roles in this article. We will also cover how to create new user roles or customize existing WordPress User Permissions. Once you understand the capabilities of WordPress User Permissions, you can easily edit them through the user screen on the WordPress dashboard.
1. The Administrator Role
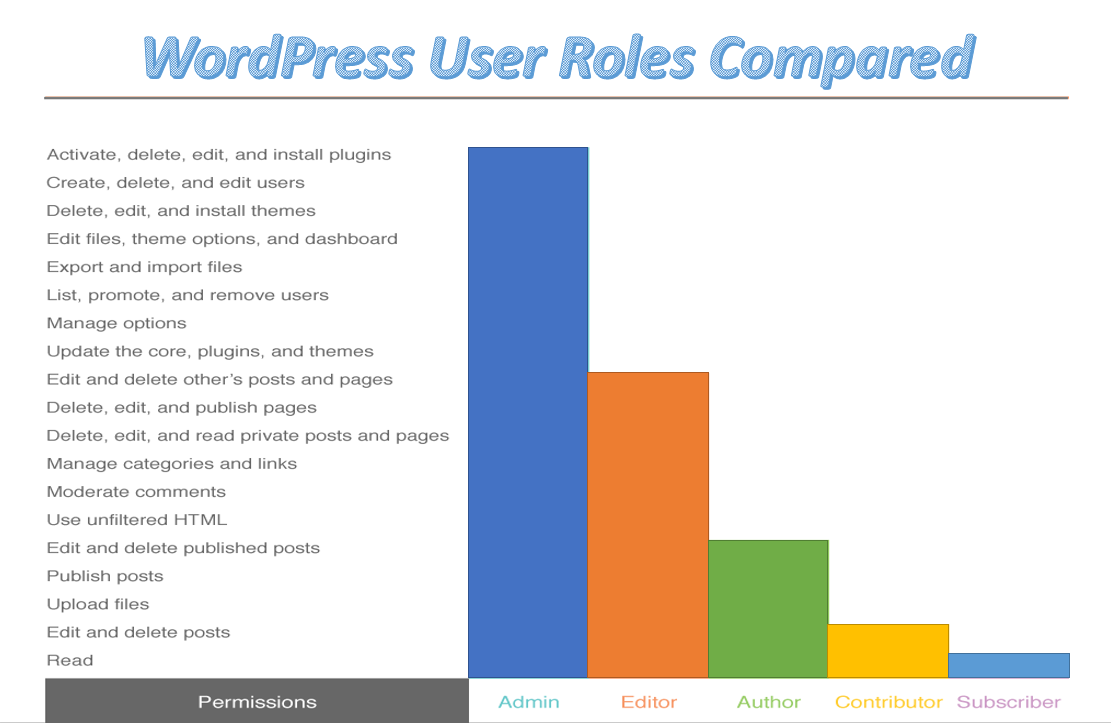
On a regular WordPress install, Administrator is the most powerful user role. The administrator is at the very top of the hierarchy. In most cases, there is only one, and they can access all the functions of the WordPress backend.
Users with the administrator role can-
- Create, edit, and delete any content
- Manage plugins and themes
- Edit code
- Modify core files, and change other users’ roles.
- Delete other user accounts
- Admins also have complete control over all content.
This role is reserved for site owners and gives you the full control of your WordPress site. If you are running a multi-user WordPress site, then you need to be very careful who you assign an administrator user role.
2. The Editor Role
Users with the editor role in WordPress have full control over your website’s content sections.

Users with the Editor role can-
- Create, edit, delete any post.
- Publish both pages and posts, even those belonging to other users.
- Moderate comments.
- Manage categories and links.
But, editors do not have access to change your site’ settings, install plugins and themes, or add new users. They are responsible for overseeing the work of authors and contributors.
3. The Author Role
An author has far fewer permissions than editors. Authors are responsible for creating content, and nothing more.
Users with the Author role can-
- Write, edit, and publish their posts.
- Also delete their own posts, even if they are published.
- Add tags to their posts
- View comments even those that are pending review
They cannot edit pages and are unable to alter other users’ content. They also can’t create categories or moderate, approve, and delete any comments.
Authors don’t have access to settings, plugins, or themes, so it is a reasonably low-risk user role on a site.
4. The Contributor Role
The contributor role is a stripped-down version of the author role. Contributors can write and edit posts, but their content must be reviewed and published by an Admin or Editor. This role is quite limited because it doesn’t enable users to publish posts or upload media files.
Users with the Contributor role only can –
- Read all posts.
- Write and edit their own posts.
- Delete them as well as.
- And view comments.
Contributors can’t even publish their own posts. Another disadvantage of a contributor role is that they cannot upload files. This role is ideal for one-time and new content creators.
5. The Subscriber Role
WordPress labels all new users as subscribers by default. They have decidedly fewer capabilities!
Users with the Subscriber role can-
- Read all posts.
- Post comments.
- And only create a profile through your WordPress dashboard.
They don’t have any permission for making further changes to your site’s admin area or adding any post and viewing comments.
6. The Super Admin Role
Last and finally there is the Super Admin Role.
This role is only applicable to Multisite installations– a network of connected WordPress sites. The super admin is responsible for the entire system and can make high-level changes.
Users with the Super Admin Role role can-
- Add and delete sites.
- Manage the network’s users.
- Select and delete themes, plugins, and more.
- Add users.
The dashboard of the super admins looks similar to a regular Administrator, but they hold more power than admins. Regular admins on WordPress Multisite networks can’t install, upload, and delete themes and plugins. They are even not allowed to modify user information. These capabilities are reserved for the super admin.
Apart from the above-mentioned roles, there are some other special roles including guest, customers, vendors, employees and many more.
You can also add custom user role on your WordPress site. Read the article to learn more about adding custom user roles!
WordPress User Management Plugins
There are some great WordPress User Management Plugins to have a bird’s eye view of every user and what each user can do.
Quick Navigation
WP User Manager
WP User Manager is one of the most popular and high rated plugins for WordPress. The plugin lets you create highly flexible and customizable user profiles. You can build custom user registration forms, login forms, custom password recovery steps and account customization forms with WP User Manager.
User Role Editor
User Role Editor enables users to change user roles and capabilities easy. The plugin provides a very easy UI where you can turn on check boxes of capabilities you wish to add for each user.
You can also add new roles and customize each user’s role according to your need.
User Switching
Want to quickly switch user roles from the WordPress dashboard? User switching is the perfect little plugin for that.
WP User Frontend
WP User Frontend is a great plugin to make sure your users always stay on the frontend and does not have to go to the WordPress dashboard for any kind of submission. Be it forms, posts or login. WPUF handles it all.
- Users can create an unlimited number of post type forms. The forms allow a user to create new posts, update a new post or edit them from the site frontend, so that the user does not need to enter the backend admin panel to do action.
Final Thoughts
Sometimes it’s important to give people access to your backend. You can’t always run your site individually. Teamwork is important. That’s why WordPress comes with built-in WordPress User Permissions. You can now authorize your users only the access they need. Applying proper WordPress User Permissions will enable you to focus more on your site’s growth and reach to more clients.
WordPress, is arguably the easiest Content Management Systems in the world. If you are not using WordPress why you should use it. Also, our beginner’s tutorials can assist you to learn more on WordPress.
Disclosure: WP Hive earns a commission when you buy through partner links. It does not influence the unbiased opinions of our writers. Learn more →
https://wphive.com/tutorials/wordpress-user-roles/
Sakil Adnan
Sakil Adnan is an Author, Content Strategist, and Editor. Completed his Graduation in Business & Marketing. Passionate about WordPress, history, religion, and literature. Enjoys exploring new things beyond regular responsibilities. Believes in teamwork and loves empowering team members. Now working as the head of content at weDevs and WPHive.




2 replies on “WordPress User Roles, Explained under 5 min!”
I went through your article which was on User Roles and Permissions in WordPress. By assigning appropriate roles and permissions to different users, you can control what actions they can perform on your site. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to manage user roles and permissions in WordPress:
1.Understanding User Roles
2.Accessing User Roles and Permissions
3.Assigning User Roles
4.Customizing User Permissions
5.Creating Custom User Roles (optional)
6.Testing User Roles
These are some points which I wanted to include in your article.
Thank you, dear reader, for taking the time to comment on our blog post! It’s through your thoughtful comments and insights that we can foster a vibrant and interactive community.